The Indian Ocean and the Arabian Sea are two of the most important bodies of water on the planet. They are located in one of the most diverse and dynamic regions of the world, connecting the continents of Asia, Africa, and Australia. For centuries, these two water bodies have been vital for human civilization, providing opportunities for trade, cultural exchange, and scientific research. In this article, we will explore the geography, history, and significance of the Indian Ocean and Arabian Sea, as well as their current challenges and opportunities.
Geography and Geology: The Indian Ocean and Arabian Sea
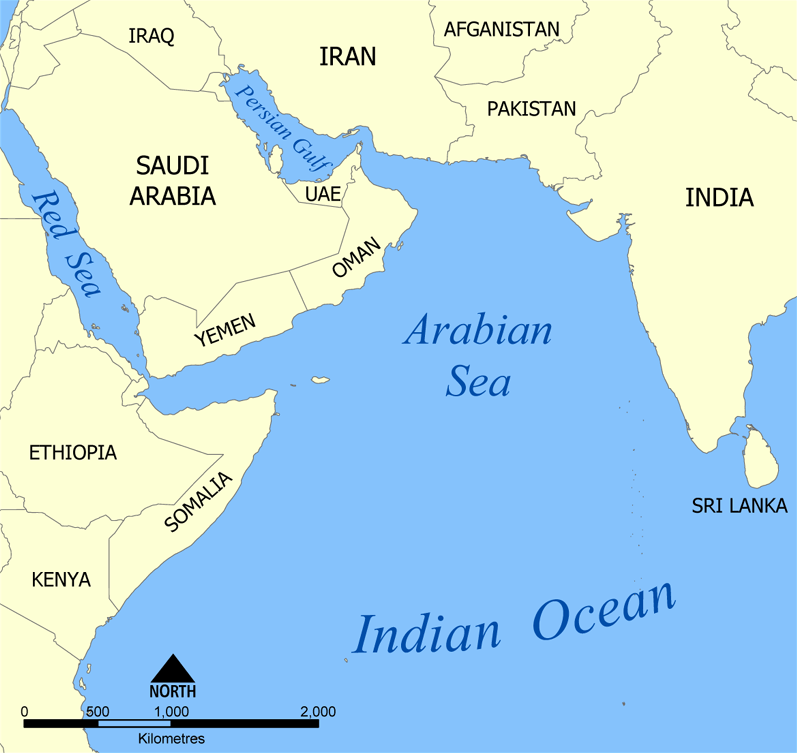
The Indian Ocean is the third largest ocean in the world, covering an area of over 70 million square kilometers. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west, and Australia to the east. The Arabian Sea is a part of the Indian Ocean, situated between the Arabian Peninsula and the Indian subcontinent. The two water bodies are connected by the Strait of Hormuz, which is one of the most strategic chokepoints in the world. The Indian Ocean and Arabian Sea are characterized by their warm waters, diverse marine ecosystems, and abundant natural resources.
History: From Ancient Trade Routes to Modern Maritime Power
The Indian Ocean and Arabian Sea have played a crucial role in the history of human civilization. For thousands of years, these water bodies have been used as a means of transportation and communication, facilitating trade and cultural exchange between different regions. The ancient trade routes of the Indian Ocean, such as the Silk Road, the Spice Route, and the Incense Route, have left a lasting impact on the economies and cultures of the countries that border the ocean. In modern times, the Indian Ocean has become a focal point for global politics and strategic competition, with major powers such as India, China, and the United States vying for influence in the region.
Commerce and Culture: The Role of the Indian Ocean and Arabian Sea in Global Trade and Exchange
The Indian Ocean and Arabian Sea are home to some of the busiest shipping lanes in the world, connecting the major ports of Asia, Africa, and Europe. The region is also known for its vibrant cultural diversity, with people from different ethnicities and religions coexisting and exchanging ideas for centuries. The Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), which was established in 1997, aims to promote economic cooperation and cultural exchange among the countries that border the Indian Ocean. The region is also home to several important institutions, such as the Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS) and the Indian Ocean Commission (IOC), which work towards enhancing security and sustainability in the region.
Climate Change and Environmental Challenges: The Impact on Ocean and Coastal Communities
The Indian Ocean and Arabian Sea are facing several environmental challenges, including climate change, pollution, overfishing, and coastal erosion. The warming of the ocean is leading to the bleaching of coral reefs, which are crucial for marine biodiversity and coastal protection. The increase in sea levels is threatening the low-lying coastal communities, while the pollution from human activities is affecting the health of marine life and the livelihoods of the coastal communities. The countries that border the Indian Ocean and Arabian Sea are working towards mitigating these challenges through measures such as marine protected areas, sustainable fishing practices, and renewable energy.
Opportunities and Future Outlook: Sustainable Development and Collaboration
The Indian Ocean and Arabian Sea region present significant opportunities for sustainable development and collaboration. The blue economy, which refers to the sustainable use of ocean resources for economic growth, is an area of focus for the region. This includes activities such as fisheries, aquaculture, tourism, and renewable energy. The region also has significant potential for developing marine biotechnology, which can contribute to the development of new drugs and therapies. Additionally, the region is home to several important research institutions, such as the National Institute of Oceanography in India and the Institute of Marine Sciences in Oman, which can collaborate on scientific research and technological innovation.
Collaboration among the countries that border the Indian Ocean and Arabian Sea is crucial for addressing the common challenges and realizing the opportunities of the region. The Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA) and other regional organizations provide platforms for dialogue and cooperation among the countries. Additionally, multilateral initiatives such as the Indian Ocean Tuna Commission and the Indian Ocean Renewable Energy Framework can facilitate sustainable management of ocean resources and promote renewable energy development.
Bibliography
- Beck, S. (2016). The Indian Ocean in World History. Routledge.
- Gopalakrishnan, C. (2019). The Indian Ocean: Oceanic Connections and the Creation of New Societies. Routledge.
- Indian Ocean Rim Association. (2021). About IORA. Retrieved from https://www.iora.int/about-iora
- Indian Ocean Tuna Commission. (2021). About IOTC. Retrieved from https://www.iotc.org/about
- International Renewable Energy Agency. (2021). Indian Ocean Renewable Energy Framework. Retrieved from https://www.irena.org/indianocean
- Koblinsky, C. J., & Brown, C. W. (Eds.). (2019). The Indian Ocean: Oceanography, Climate, and Ecosystem Dynamics. AGU Wiley.
- United Nations Environment Programme. (2019). The Indian Ocean: The Future We Want. Retrieved from https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/28163/The_Indian_Ocean_The_Future_We_Want.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y


 For all latest articles, follow on Google News
For all latest articles, follow on Google News